Conservatories are a popular addition to many homes in the UK, offering a bright and airy space that can be enjoyed as an extension of the home.
However, one of the key challenges homeowners face with conservatories is maintaining a comfortable temperature, whether it’skeeping the space cool in summer or warm in winter.
This is where U-values come into play. Understanding U-values and their impact on energy efficiency is important for anyone looking to improve their conservatory’s insulation.
In this blog, we’ll answer the question “what is U-value?”, looking at why they matter and how they affect your conservatory’s energy efficiency.
What is U-value?
U-value measures how well a building material can conduct heat. It can be used to understand the rate of heat transfer through a structure, such as a roof, wall, or window.
The lower the U-value, the better the material is at insulating. If the U-value is high, the material is less energy efficient.
Essentially, a low U-value means less heat is lost in winter, and less heat is gained in summer, leading to a more energy efficient and comfortable conservatory.
Why U-value matters for conservatories
U-values are particularly important for conservatories because these spaces often have large areas of glazing and roofing that can be susceptible to heat loss and gain.
Efficient insulation is essential to reduce energy consumption and maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Choosing materials with low U-values can help you make sure that your conservatory remains usable throughout the year without incurring high heating and cooling costs.
How to calculate U-value
Calculating the U-value of a building element involves understanding the thermal conductivity of the materials used and the thickness of each layer.
To calculate the U-value for a conservatory roof composed of three layers – an outer weatherproof layer, an insulation layer, and an inner finishing layer – we would look at the below information and make a calculation.
| Layer | Material | Thickness (d) | Thermal Conductivity (k) |
| Outer | Weatherproof membrane (e.g., bitumen felt) | 10 mm (0.01 m) | 0.17 W/m x K |
| Insulation | Rigid foam insulation (e.g., polyurethane foam) | 100 mm (0.1 m) | 0.025 W/m x K |
| Inner | Plasterboard | 12.5 mm (0.0125 m) | 0.21 W/m x K |
Using these materials as an example, the calculated U-value for the conservatory roof would be approximately 0.243 W/m² x K.
This is a low U-value, and it indicates good thermal insulation, meaning the roof is effective at preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Overall, this contributes to a more energy-efficient and comfortable conservatory.
Choosing materials with low thermal conductivity and sufficient thickness gives homeowners a way to improve their conservatory’s thermal performance.
Insulated roof panels, like those offered by CosyPanels, typically have the lowest U-value among conservatory roofing options, making them an excellent choice for enhancing energy efficiency all year round.
Free U-value calculator
If manual calculations seem daunting, there are several online tools available to help. A handy resource is the U-value calculator, which simplifies the process by allowing you to input the materials and their dimensions to get an accurate U-value.
Understanding G-values
While U-values measure heat transfer, G-values (or solar gain values) measure how much solar radiation passes through a material. In the context of conservatories, G-values are important because they impact how much heat from the sun enters the space.
The relationship between U value and G value
U-values and G-values together determine the overall energy efficiency of a conservatory. A material with a low U-value and an appropriate G-value will provide good insulation while still allowing some solar heat to enter, reducing heating costs in winter.
Impact of G values on conservatory design
Selecting materials with suitable G-values can help improve the comfort of your conservatory. For instance, glazing with a high G-value will let in more solar heat, which can be beneficial in colder months. Conversely, in warmer climates, a lower G-value might be preferred to prevent overheating.
Choosing the right U-value for conservatory roofing
When it comes to conservatory roofing, different materials have varying U-values. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed choice.
Comparison of different roofing materials
Polycarbonate roofing: This is a popular option due to its affordability and lightweight nature. However, polycarbonate has a relatively high U-value (around 2.4 W/m²K), meaning it is less effective at insulating compared to other materials.
Glass roofing: Standard double glazing typically has a U-value of around 2.8 W/m²K, while triple glazing can achieve U-values as low as 0.6 W/m²K. Glass roofs provide better insulation than polycarbonate and can also be treated to improve their G values.
Insulated roof panels: These panels can have U-values as low as 0.18 W/m²K, making them one of the most energy-efficient options available. They combine layers of insulation with a weatherproof outer layer to offer a great thermal performance.
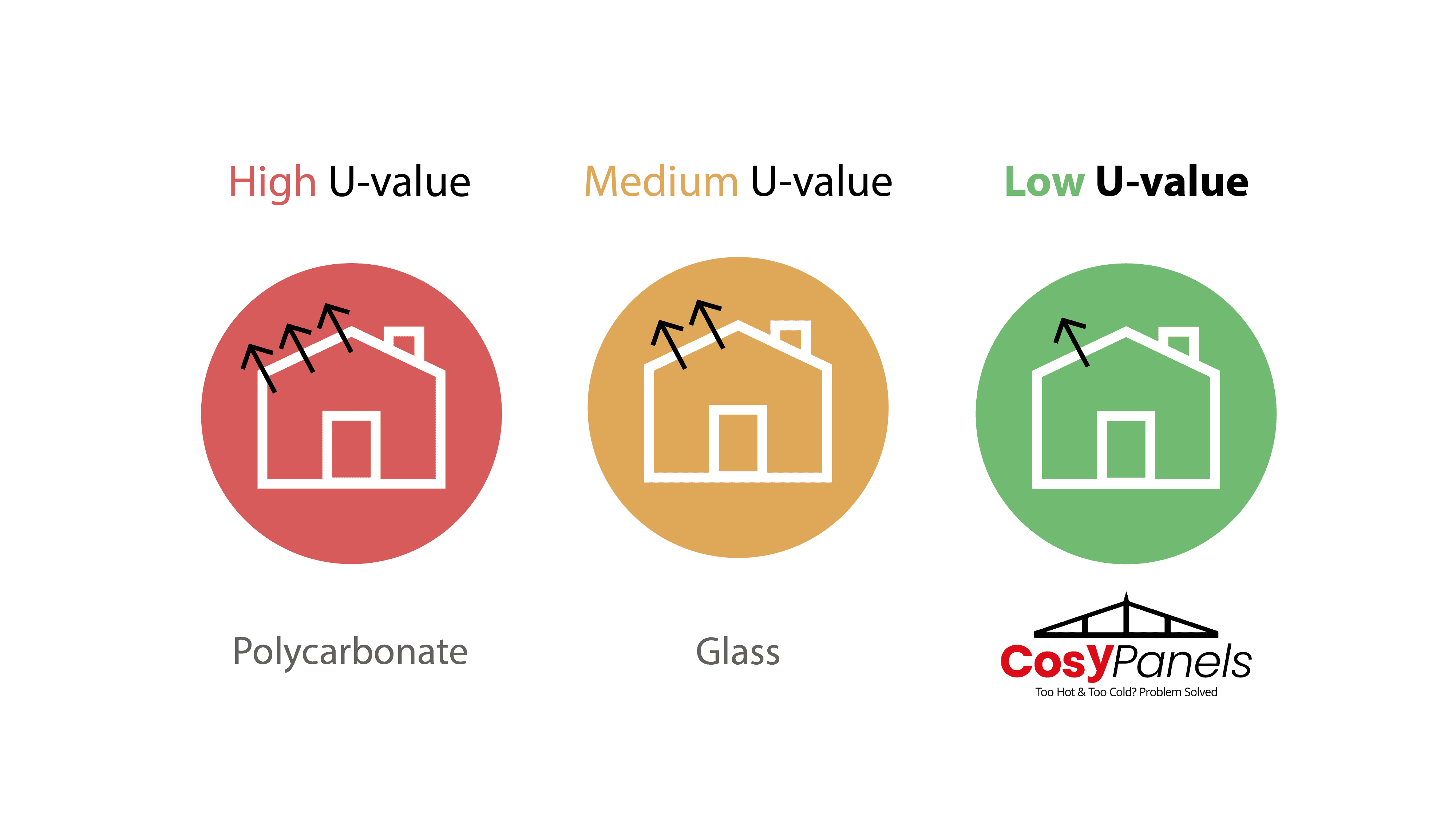
What is the most energy-efficient conservatory roof option?
For the most energy-efficient conservatory roof, insulated roof panels stand out due to their excellent U-values. These panels not only provide superior thermal insulation but also help in reducing overall energy costs.
Top roofing materials and their U-values
- Polycarbonate: ~2.4 W/m²K
- Double Glazed Glass: ~2.8 W/m²K
- Triple Glazed Glass: ~0.6 W/m²K
- Insulated Roof Panels: ~0.18 W/m²K
Innovations in conservatory roof design
Recent innovations in conservatory roof design focus on improving energy efficiency and comfort. New materials and construction techniques are continually being developed to provide better insulation and durability.
Vacuum-insulated panels
Vacuum-insulated panels which can offer even lower U-values than traditional insulated panels. Vacuum insulated panels are high-performance thermal insulation panels that use a vacuum to achieve extremely low thermal conductivity. Each panel consists of a core material, usually fumed silica or a similar porous substance, encased in a gas-tight envelope. The air inside the panel is evacuated to create a vacuum, drastically reducing the heat transfer through the panel.
Solar control glass
Solar control glass is an innovative product that helps regulate the amount of solar energy entering the conservatory. This type of glass has special coatings that reflect a large portion of the sun’s heat, stopping the interior from becoming excessively hot during sunny days. It also allows natural light to pass through, keeping it bright and airy without the accompanying heat.
CosyPanels
Thermally efficient roofing panels are designed to offer high insulation, reduce heat loss in the winter, and keep the space cooler in the summer. Products like CosyPanels are excellent examples, providing high U-values that ensure better thermal performance. These panels often include features such as:
Sandwich panels
Insulated sandwich panels are made with a core insulating material (like rigid foam) sandwiched between two layers of durable outer material.
Smart glass
Dynamic glass, also known as smart glass, can change its tint in response to sunlight or can be controlled manually via a smartphone or other devices. This technology allows homeowners to adjust the amount of light and heat entering the conservatory, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency.
For more insights into future conservatory innovations, check out this article on conservatories of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the U-value of a triple-glazed conservatory?
Triple-glazed conservatories typically have U-values around 0.6 W/m²K, making them extremely effective at insulating against heat loss.
How do you get a 0.18 U-value roof?
Achieving a U-value of 0.18 W/m²K generally involves using advanced insulated roof panels. These panels are designed with multiple layers of insulation materials that work together to provide a high thermal performance.
What is the U-value of a glass roof?
The U-value of a glass roof can vary depending on the type of glazing. Standard double glazing has a U-value of about 2.8 W/m²K, while more advanced triple glazing can achieve U-values as low as 0.6 W/m²K.
How much heat is lost through a polycarbonate conservatory roof?
Polycarbonate roofs have a higher U-value, typically around 2.4 W/m²K, which means they are aren’t the best for preventing heat loss compared to glass or insulated panels. This can result in significant heat loss during colder months.
Make an informed decision for your conservatory roof
Understanding U-values is essential for making informed decisions about conservatory roofing. By selecting materials with low U-values, you can truly improve the energy efficiency and comfort of your conservatory.
Insulated roof panels, such as those offered by CosyPanels are some of the best when it comes to dealing with extreme temperatures, making them an excellent choice for homeowners looking to make improvements to their conservatories.
Whether you’re planning a new build or upgrading an existing structure, understanding and getting the best from U-values is a good way of ensuring you create a conservatory that really complements your lifestyle and stands the test of time.
For more information on the best solutions for your conservatory, visit CosyPanels.


